The Opportunities and Challenges In the Health Insurance Industry
Currently, health insurance in India is still very low, and the increasing costs of healthcare make the service very expensive. Tapan Singhel, MD & CEO of Bajaj Allianz General Insurance, for example, has called for aggressive policy measures, as has Srinivasan Gopalan, MD & CEO of Galaxy Health Insurance Company. These changes are intended to protect the “missing middle”—an area of the population that is most at risk because of insufficient insurance.
Singhel supported insurance by encouraging people to consider it as a basic need rather than a want. He said high GST rates on insurance premiums discourage many from getting the necessary coverage.
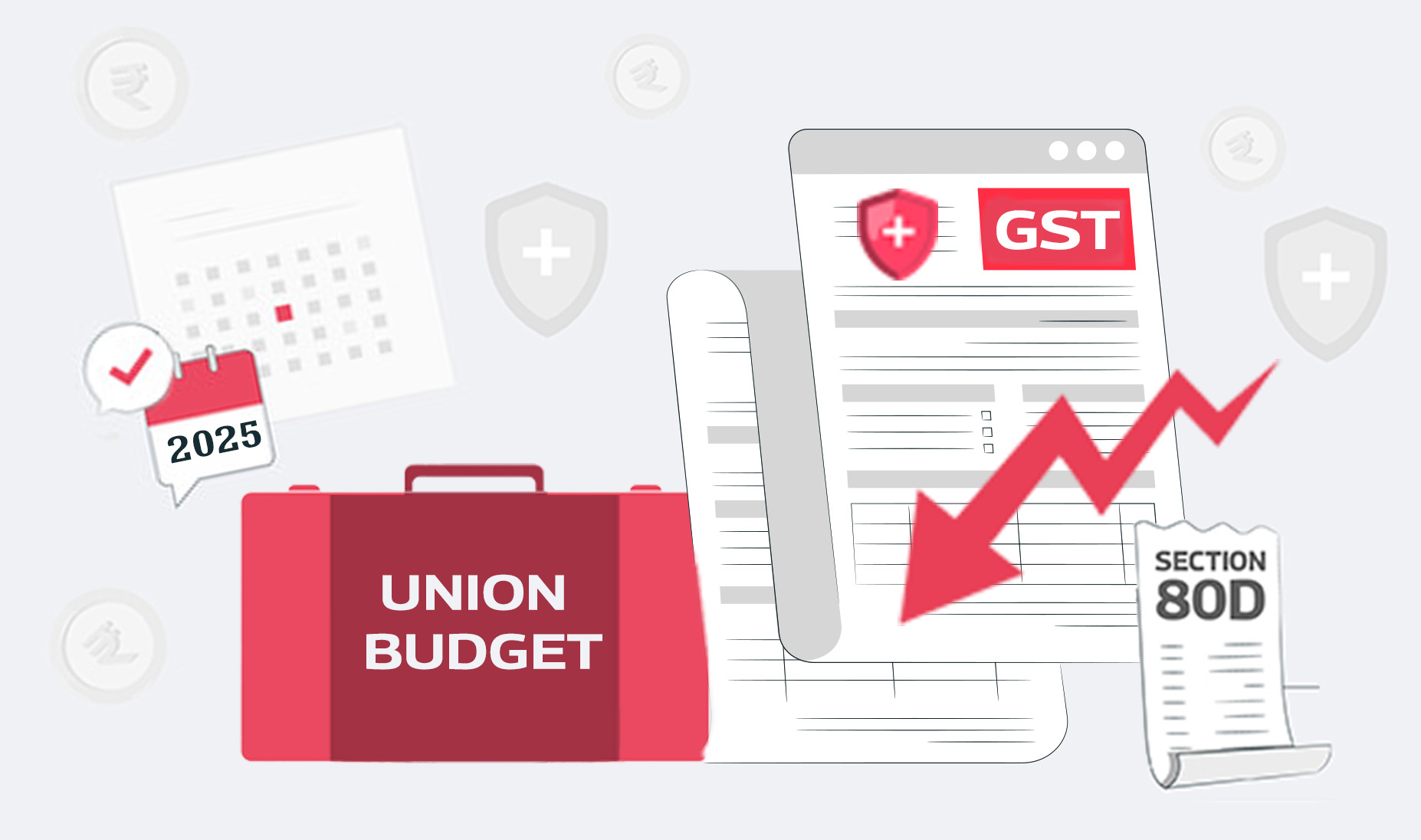
The Key Expectations from Budget 2025
1.Reduction in GST on Health Insurance Premiums
The sector is lobbying for the GST rate on health insurance premiums, which is pegged at 18%, to be slashed. This rate could be reduced to make policies cheaper and thus available to many people in the population.
“If a GST cut is not possible, other options the government should explore include Section 80D of the Income Tax Act, which allows businesses to deduct the entire amount paid for medical insurance.” These changes could stimulate greater usage without much effect on the government’s income.
2. Amendments in Section 80D of the Income Tax Act
- Raising the limit of deduction for health insurance premiums to ₹50,000 for any individual and ₹1,00,000 for senior citizens.
- Expanding Section 80D to cover the new tax slabs to ensure that claimed exemptions on health insurance are not constrained to a particular income category.
Srinivasan Gopalan also moved to amend Rule 6E, which concerns unexpired premium reserves. He proposed using the 1/365 approach in determining reserves, as per the IRDAI financial reporting standards for insurance firms.
3. More General Tax Exemptions on Insurance Products
To promote financial protection, Singhel suggested providing 100% tax exemptions for premiums paid on various protection-oriented products, including:
“These measures would encourage people to spend on personal protection and, in the process, increase insurance penetration as well as financial depth,” he pointed out.
4.Formation of a Health Regulator
One major expectation from the sector is the innovation of a health regulator to effectively tackle issues, including medical inflation and the variation in hospital pricing. Increasing costs related to healthcare have remained the most significant threat to insurers due to hospitalisation costs, which have kept insurers struggling to balance the pricing of their products because adjustments are only done once in three years.
“Creation of a regulatory body to manage hospitals would make prices and quality of services more uniform and affordable for all people,” Singhel added. Stakeholders’ consultations between the NHA, IRDAI, and others are being held regarding this matter, and people are expecting a positive result soon.
The Increased Healthcare Expenses: A Proposal
Medical inflation has been a key issue, with costs sometimes rising by up to 15% during a three-year pricing cycle. These inflations have cost implications for both policyholders and insurers. A health regulator could fill the gap by putting through fair tariffs and ensuring proper mediation for medical treatment.
.png)



.png)